
StereoBM
立体匹配-BM算法
立体匹配相关算法
常见立体匹配算法流程
常见的立体匹配算法主要包括以下四步
- 匹配代价计算
- 代价聚合
- 视差计算或优化
- 视差改良
匹配代价计算常采用sad等方法,根据左右两幅图像上匹配点的像素之差的绝对值。
代价聚合常采用一个固定窗口,计算窗口内部的所有视差之和。
视差的计算最直观的方式是采用WTA(Winner Takes All)的方式,直接选取使得聚合代价最小的视差值。
未完。。。。待续。。。
内容详见论文[1].
BM算法概括
简单的理解立体匹配,在行对准的两幅图像中找到同一个点,或Reference图像中给定一点,在Target图像中搜索对应的点,如下图所示。
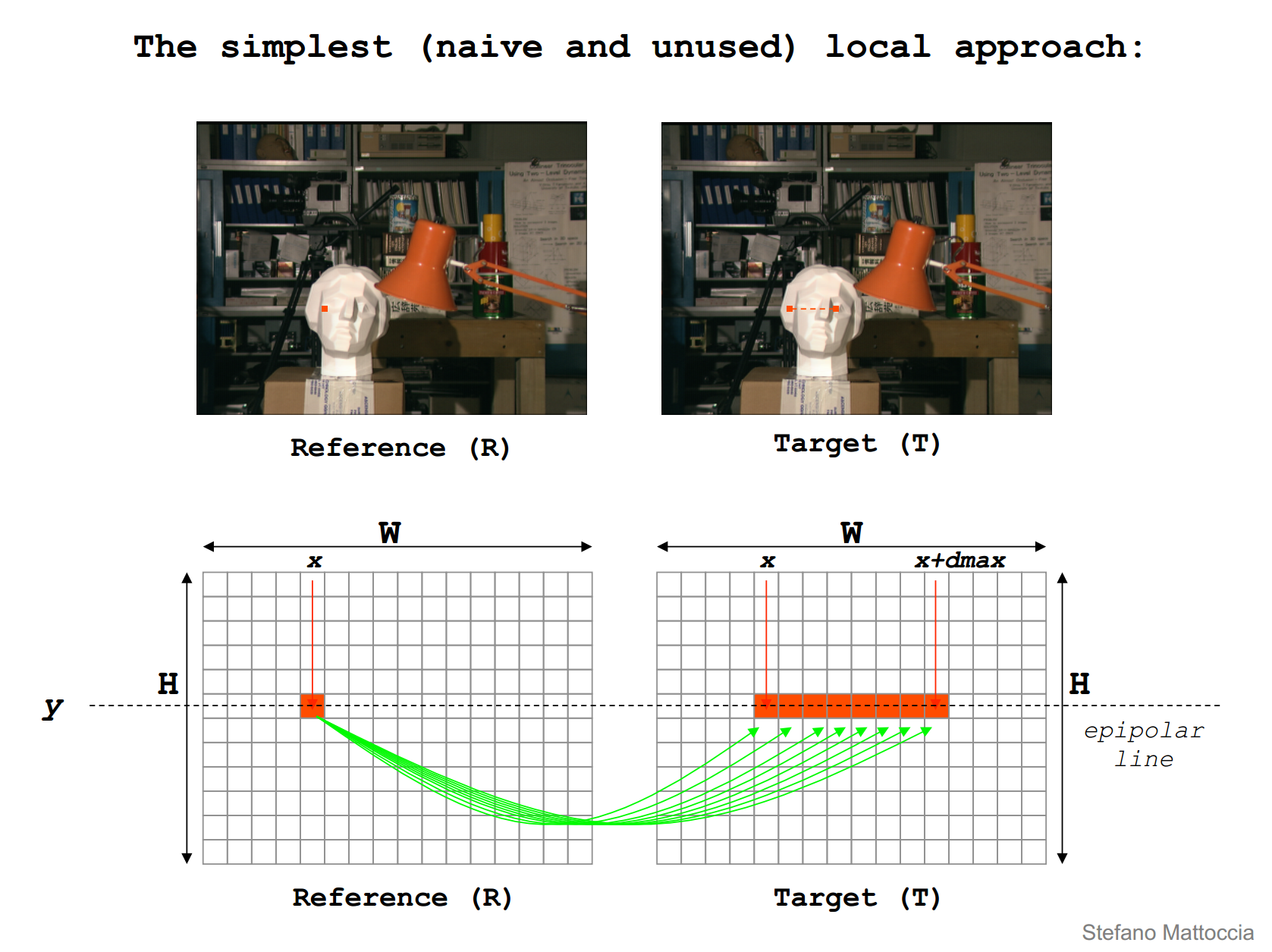
实际上,直接对一点来进行匹配,百分百会出现各种各样的问题,这个时候我们选择用一个固定窗口来替代一点,如下图所示。
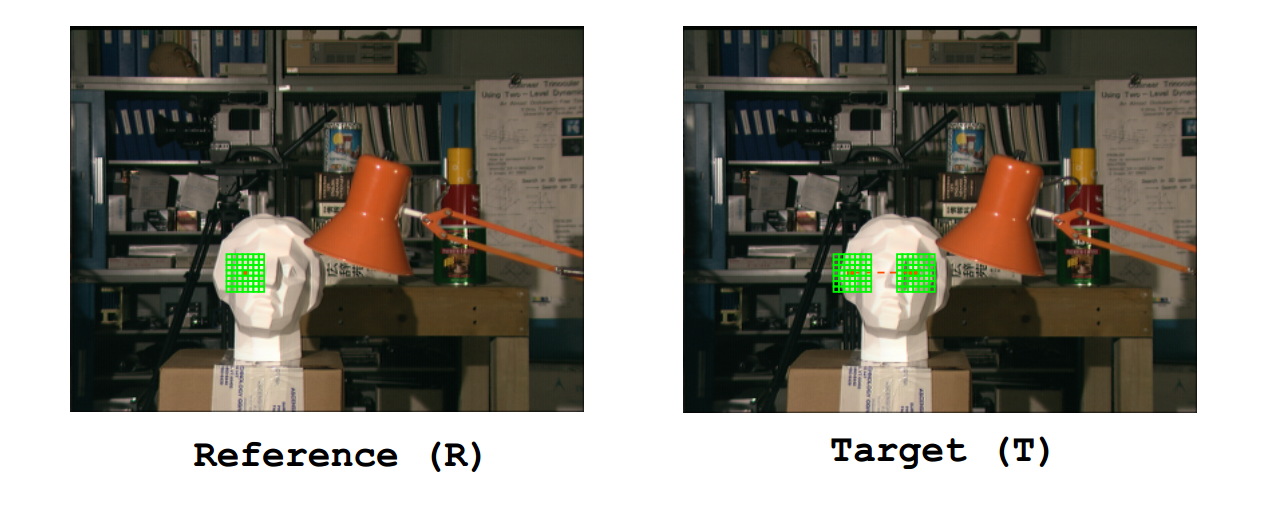
Warning,这样做就隐含了一个假设,认为窗口内部视差值相同,但是,显然的,这种假设太过想当然,也使得算法实际效果不好。
BM算法,也常称为SAD(Sum of Absolute Differences)算法,是双目立体匹配中最基本的算法。
下面简要介绍该算法的原理、直观算法实现、opencv接口介绍以及opencv源码的实现。
SAD基本理论
强烈推荐,文献[2],本文可以说是对文献2的几页ppt进行了翻译。
SAD算法由3步构成。
- 匹配代价计算
- 代价聚合
- 视差计算
是不是很熟悉?实际上很多双目算法都可以这样划分。
Matching Cost Computation
SAD的匹配代价计算比较简单,Reference图像和Target图像像素直接相减加绝对值,即$|I_R(x,y)-I_T(x+d,y)|$。
视差空间(DSI)是一个三维矩阵,定义
| [c(x,y,d)= | I_R(x,y)-I_T(x+d,y) | ] |
可以理解为Reference图像$(x,y)$点,在搜索视差为$d$时的代价。
Cost Aggeration
SAD的代价聚合就是将固定窗口FW(Fixed Window)内代价求和,直观理解如下图所示。
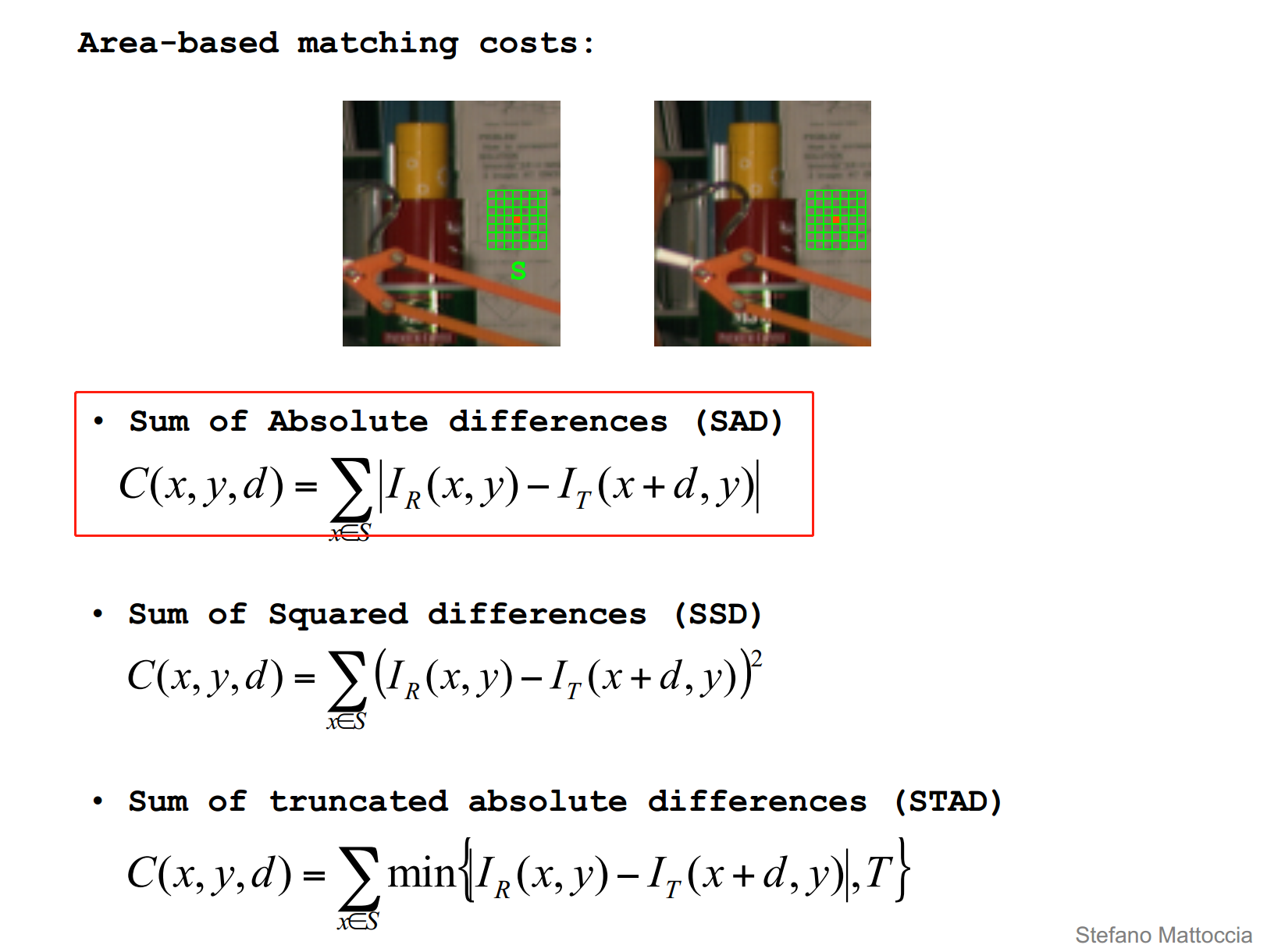
计算FW内视差视差为d时的聚合代价
[C(x,y,d)=\sum_{x\in S}|I_R(x,y)-I_T(x+d,y)|]
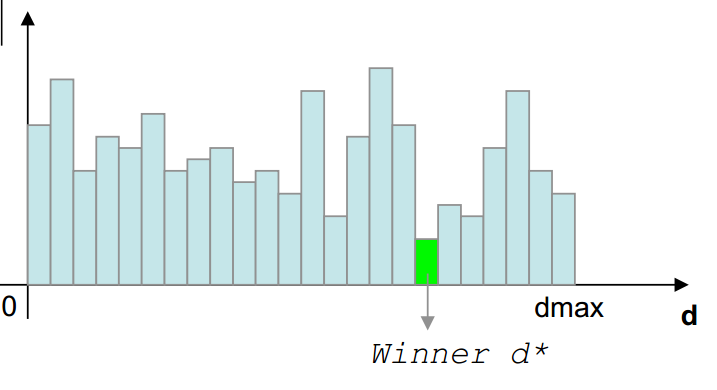
Disparity Computation
SAD的视差计算非常简单,采用WTA原则,对于给定的$(x,y)$,找使得$C(x,y,d)$最小的d,此d即可认为时该点的视差。
直观算法实现
好,大概理论说完了,现在说一下直观算法实现,本节主要参考了文献[3]和[4]。
代码很好理解,直接从两幅图像取两个Rect相减,求绝对值,循环遍历找到使其最小的视差,代码简单,运算速度很慢。
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
class SAD
{
public:
SAD() :winSize(7), DSR(30) {}
SAD(int _winSize, int _DSR) : winSize(_winSize), DSR(_DSR) {}
Mat computerSAD(Mat &L, Mat&R);
private:
int winSize; //卷积核尺寸
int DSR; //视差搜索范围
};
Mat SAD::computerSAD(Mat&L, Mat& R)
{
int height = L.rows;
int width = L.cols;
Mat kernel_L(Size(winSize, winSize), CV_8U, Scalar::all(0));
Mat kernel_R(Size(winSize, winSize), CV_8U, Scalar::all(0));
Mat disparity(height, width, CV_8U, Scalar::all(0));
for (size_t i = 0; i < width - winSize; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < height - winSize; j++)
{
kernel_L = L(Rect(i, j, winSize, winSize));
Mat MM(1, DSR, CV_32F, Scalar(0));
for (size_t k = 0; k < DSR; k++)
{
if (i >= k)
{
kernel_R = R(Rect(i - k, j, winSize, winSize));
Mat Dif;
absdiff(kernel_L, kernel_R, Dif);
Scalar ADD = sum(Dif);
MM.at<float>(k) = ADD[0];
}
}
Point minLoc;
minMaxLoc(MM, NULL, NULL, &minLoc, NULL);
int loc = minLoc.x;
disparity.at<char>(j, i) = loc * 16;
}
}
return disparity;
}
这里还有一篇SAD的实现见[4]。相比上一篇多了一个Left-Right Consistency,代码很好理解,直接贴上来。
#pragma once
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
float sadvalue(const Mat& src1, const Mat& src2)
{
Mat matdiff = cv::abs(src1 - src2);
int saddiff = cv::sum(matdiff)[0];
return saddiff;
}
float GetMinSadIndex(vector<float>& sad)
{
float minsad = sad[0];
int index = 0;
int len = sad.size();
for (size_t i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
if (sad[i] < minsad)
{
minsad = sad[i];
index = i;
}
}
return index;
}
void MatDataNormal(const Mat& src, Mat& dst)
{
normalize(src, dst, 255, 0, NORM_MINMAX);
dst.convertTo(dst, CV_8UC1);
}
void GetPointDepthRight(Mat& disparity, Mat& leftimg, Mat& rightimg, const int MaxDisparity, const int winsize)
{
int row = leftimg.rows;
int col = leftimg.cols;
if (leftimg.channels() == 3 && rightimg.channels() == 3)
{
cvtColor(leftimg, leftimg, CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(rightimg, rightimg, CV_BGR2GRAY);
}
int w = winsize;
int rowrange = row - w;
int colrange = col - w - MaxDisparity;
for (size_t i = w; i < rowrange; i++)
{
int *ptr = disparity.ptr<int>(i);
for (size_t j = w; j < colrange; j++)
{
Mat rightwin = rightimg(Range(i - w, i + w + 1), Range(j - w, j + w + 1));
vector<float> sad(MaxDisparity);
for (size_t d = j; d < j + MaxDisparity; d++)
{
Mat leftwin = leftimg(Range(i - w, i + w + 1), Range(d - w, d + w + 1));
sad[d - j] = sadvalue(leftwin, rightwin);
}
*(ptr + j) = GetMinSadIndex(sad);
}
}
}
void GetPointDepthLeft(Mat& disparity, Mat& leftimg, Mat& rightimg, const int MaxDisparity, const int winsize)
{
int row = leftimg.rows;
int col = leftimg.cols;
if (leftimg.channels() == 3 && rightimg.channels() == 3)
{
cvtColor(leftimg, leftimg, CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(rightimg, rightimg, CV_BGR2GRAY);
}
int w = winsize;
int rowrange = row - w;
int colrange = col - w - MaxDisparity;
for (size_t i = w; i < rowrange; i++)
{
int *ptr = disparity.ptr<int>(i);
for (size_t j = MaxDisparity + w; j < colrange; j++)
{
Mat leftwin = leftimg(Range(i - w, i + w + 1), Range(j - w, j + w + 1));
vector<float> sad(MaxDisparity);
for (size_t d = j; d > j - MaxDisparity; d--)
{
Mat rightwin = rightimg(Range(i - w, i + w + 1), Range(d - w, d + w + 1));
sad[j - d] = sadvalue(leftwin, rightwin);
}
*(ptr + j) = GetMinSadIndex(sad);
}
}
}
// Left-Right Consistency
void CrossCheckDisparity(const Mat& leftdisp, const Mat& rightdisp, Mat& lastdisp, const int MaxDisparity, const int winsize)
{
int row = leftdisp.rows;
int col = rightdisp.cols;
int w = winsize;
int rowrange = row - w;
int colrange = col - MaxDisparity - w;
int diffthreshold = 2;
for (size_t i = w; i < row - w; i++)
{
const int *ptrleft = leftdisp.ptr<int>(i);
const int *ptrright = rightdisp.ptr<int>(i);
int *ptrdisp = lastdisp.ptr<int>(i);
for (size_t j = MaxDisparity + w; j < col - MaxDisparity - w; j++)
{
int leftvalue = *(ptrleft + j);
int rightvalue = *(ptrright + j);
int diff = abs(leftvalue - rightvalue);
if (diff>diffthreshold)
{
*(ptrdisp + j) = 0;
}
else
{
*(ptrdisp + j) = leftvalue;
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
Mat img_L = imread("0.png", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
Mat img_R = imread("4.png", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
//Mat img_L = imread("aloeL.jpg", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
//Mat img_R = imread("aloeR.jpg", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (img_L.empty() || img_R.empty())
{
exit(-1);
}
Mat disparity;
/***************************************************************************/
// SAD简易实现版本+LRC
/***************************************************************************/
int row = img_L.rows;
int col = img_L.cols;
Mat depthleft = Mat::zeros(row, col, CV_32S);
Mat depthright = Mat::zeros(row, col, CV_32S);
Mat lastdisp = Mat::zeros(row, col, CV_32S);
int MaxDisparity = 64;
int winsize = 15;
GetPointDepthLeft(depthleft, img_L, img_R, MaxDisparity, winsize);
GetPointDepthRight(depthright, img_L, img_R, MaxDisparity, winsize);
CrossCheckDisparity(depthleft, depthright, lastdisp, MaxDisparity, winsize);
MatDataNormal(depthleft, depthleft);
MatDataNormal(depthright, depthright);
MatDataNormal(lastdisp, lastdisp);
namedWindow("left", 0);
namedWindow("right", 0);
namedWindow("depthleft", 0);
namedWindow("depthright", 0);
namedWindow("lastdisp", 0);
imshow("left", img_L);
imshow("right", img_R);
imshow("depthleft", depthleft);
imshow("depthright", depthright);
imshow("lastdisp", lastdisp);
waitKey(0);
OpenCV-BM源码
opencv的bm源码进行了优化,主要是采用了Box-Filter的方法,处理速度大幅度提高,见下图。
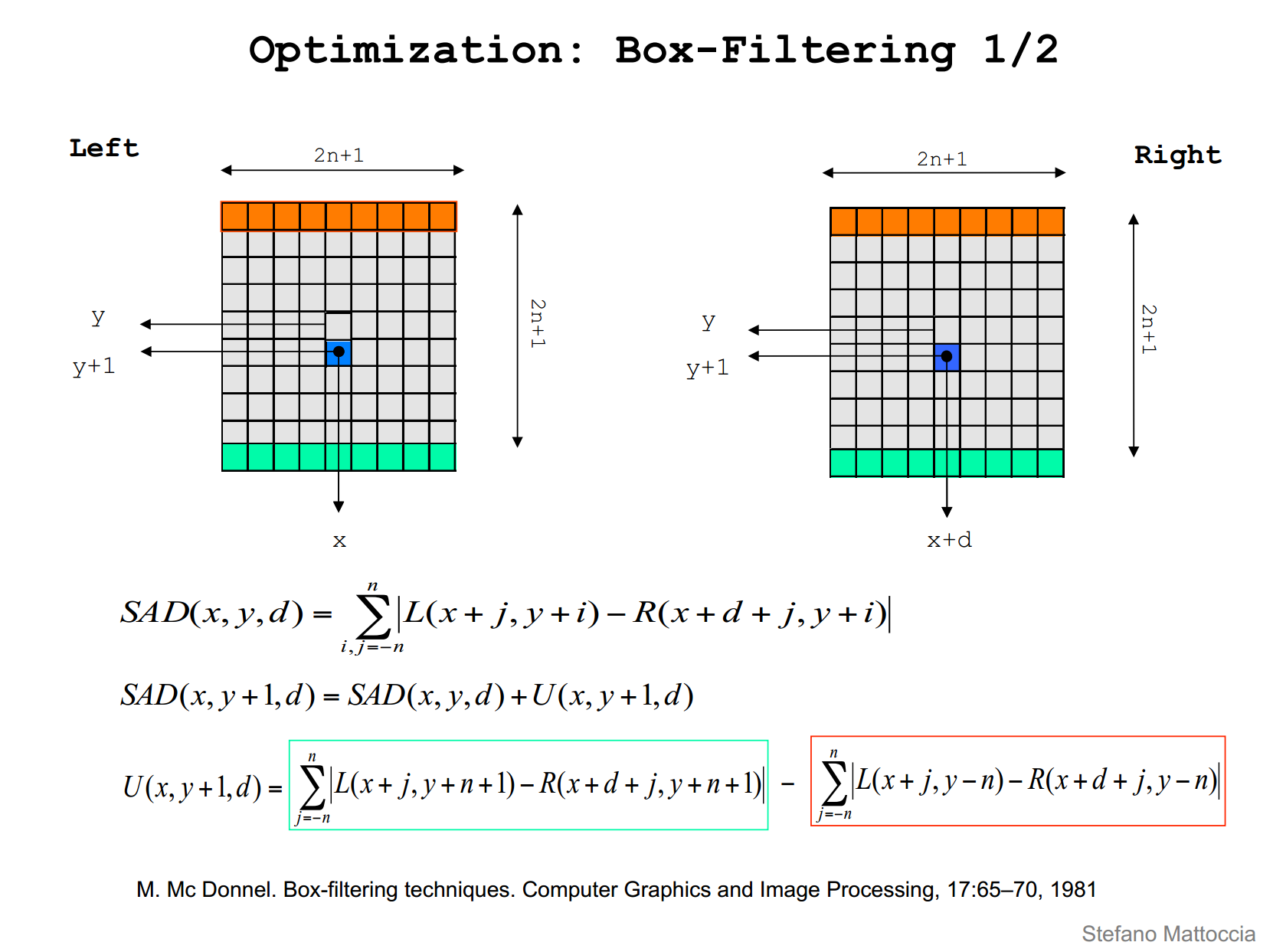
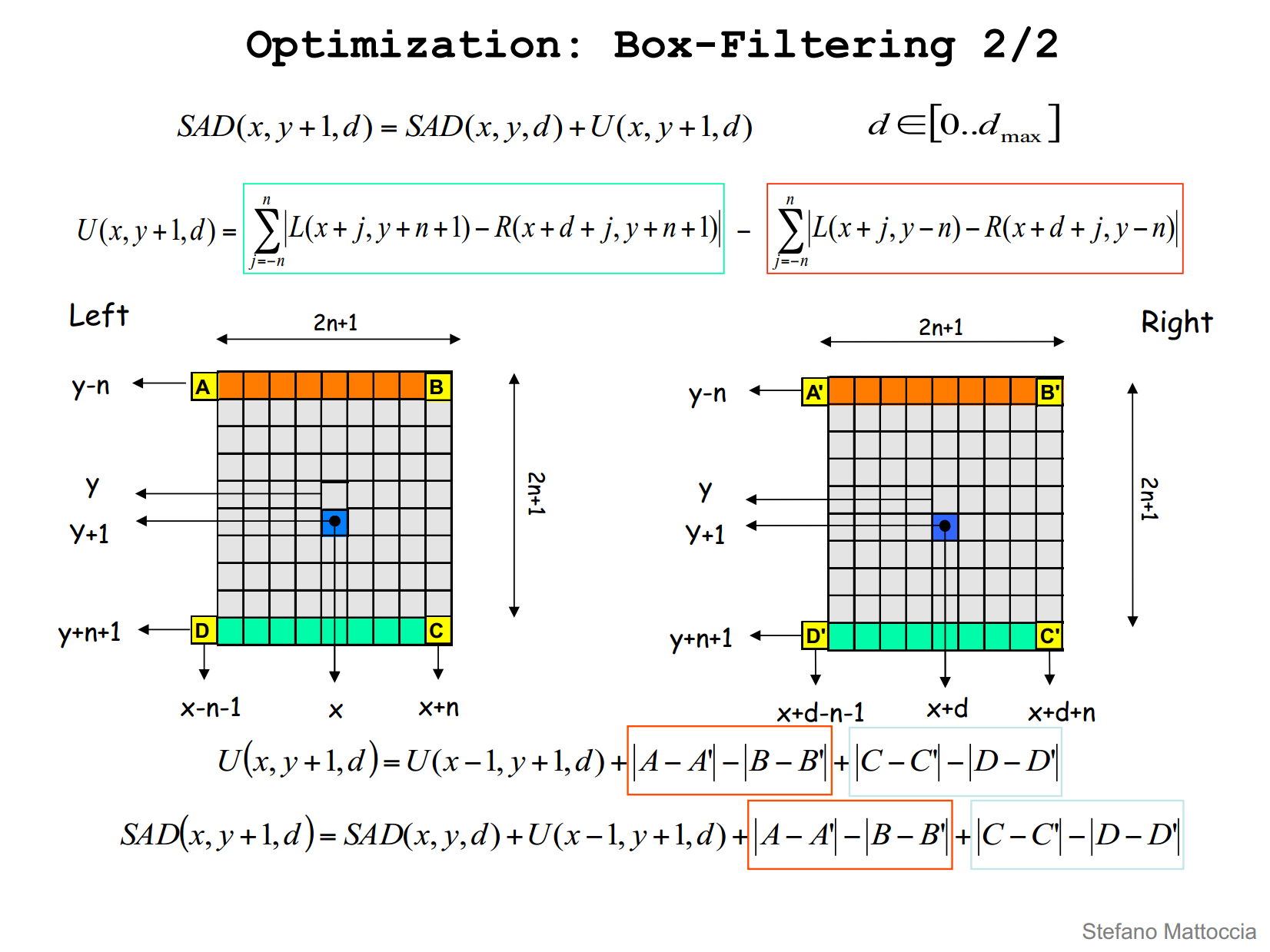
理解了这个方法再来看这段源码,就十分好理解了。
opencv的bm源码主要包括
- 参数检查
- 图像预处理(prefilterNorm和prefilterXSobel)
- 计算视差图(findStereoCorrespondenceBM):这部分当中还加入了唯一性约束
if (uniquenessRatio > 0) { int thresh = minsad + (minsad * uniquenessRatio / 100); for (d = 0; d < ndisp; d++) { if ((d < mind - 1 || d > mind + 1) && sad[d] <= thresh) break; } if (d < ndisp) { dptr[y*dstep] = FILTERED; continue; } }以及对视差不连续情况的处理
int p = sad[mind + 1], n = sad[mind - 1]; d = p + n - 2 * sad[mind] + std::abs(p - n); dptr[y*dstep] = (mType)(((ndisp - mind - 1 + mindisp) * 256 + (d != 0 ? (p - n) * 256 / d : 0) + 15) >> (DISPARITY_SHIFT_32S - disp_shift)); costptr[y*coststep] = sad[mind];
但是该算法实际在使用的时候速度足够但效果不好。
Code
代码先还没发布,等这一系列写完再推送到我的github上。
引用
[1] D. Scharstein and R. Szeliski. A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. International Journal of Computer Vision, 47(1/2/3):7-42, April-June 2002.
[2] http://vision.deis.unibo.it/~smatt/Seminars/StereoVision.pdf
[3] https://blog.csdn.net/lwx309025167/article/details/78387879?locationNum=9&fps=1
[4] http://www.cnblogs.com/adong7639/p/4267326.html